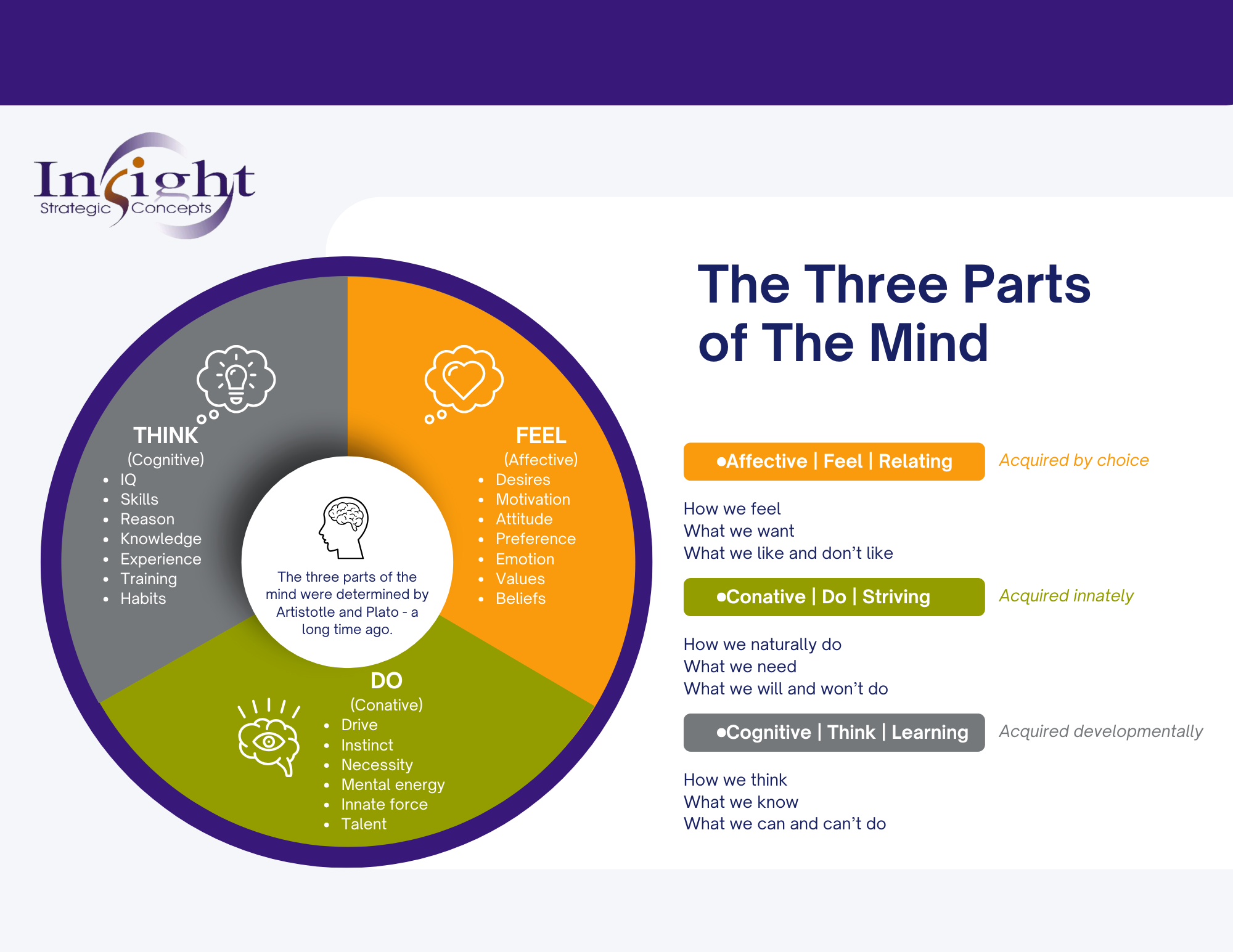
The Three Parts of The Mind
Long ago, experts in the field of psychology (Plato, Aristotle, etc.) determined that there are three parts of the mind that we each have. These three parts make up our whole person. These three parts represent how we feel, do, and think during our individual creative processes. What we feel impacts how we will do and that influences what we think (in that order). As complex human beings, these traits combine to be unique from person to person and are hard to detect in shorter windows of time without the help of reliable assessment tools.
Affective (Relating "Feel" Style)
A person’s affective strengths lie in their ability to use emotion effectively. Assessments such as the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator measure a person’s reaction to circumstances and assigns a “personality type” that defines the emotional tools that you use to cope, grow and communicate in your daily life. Like the cognitive mind, your affective traits evolve and fluctuate given your experiences and circumstances.
A person acquires these by choice.
Personality
Attitudes
Emotions
Wants
Desires
Preferences
Values
Beliefs
Feelings
Motivations
Social styles
Ways of caring
Likes and dislikes
Examples of affective assessments:
DiSC
ProfileXT (Behavioral Traits)
Myers-Briggs
Profiles Performance Indicator
Profiles Sales & Customer Service
Profiles Step One
StrengthsFinder
Working Genius
Leadership Practices Inventory (LPI)
Conative (Striving "Do" Talents)
We didn’t invent the conative mind. But our founder, Kathy Kolbe, and our team of psychologists have come to understand how it works and how to measure it. Your conative mind contains the instincts and innate attributes that define your natural method of operation (MO). When you work in your natural style, you are more productive, more comfortable and more successful. We identify people’s instinctive strengths, explain them, analyze how they align with tasks and other people, and offer practical solutions for putting them into practice — from doing better in a job, to team performance, to personal relationships.
A person acquires these innately.
How one acts
Behaviors
Actions
Natural talents
Uses of time
How one strives
Performances
Instincts
How one avoids
Forces, drives, urges
Necessities
Natural ways of doing
Innate forces
Commitments
Self-control
The executive brain
Mental energies
Inclinations
Will or won’t do
“God-given gifts”
Examples of conative assessments:
Kolbe Wisdom Kolbe Indexes A, B and C
Cognitive (Thinking "Think" Skills)
This part of your mind defines your “intelligence.” It grows as you learn and is ever-changing. IQ tests are the most common form of testing; however, anyone who has taken a test more than once knows that the results only showcase a portion of a person’s true ability to learn, retain, and recall information.
A person acquires these developmentally.
Education
Training
Skills
Experiences
Reasoning
Habits
Thinking styles
Learning styles
Knowledge
Learned behaviors
Biography – Data
Applications
Judgments
Understanding
Memories
Can and can’t do
Examples of cognitive assessments:
ProfileXT (Thinking Style)
Thomas-Kilmann Conflict Style
Hermann Brain Dominance
Various skill tests
IQ tests
>>Read more about the Insight Whole Mind recruiting and selection process
Source: Our work about The Three Parts of Mind is derived from Kolbe Corp.